Autonomic Nervous System Pharmacology
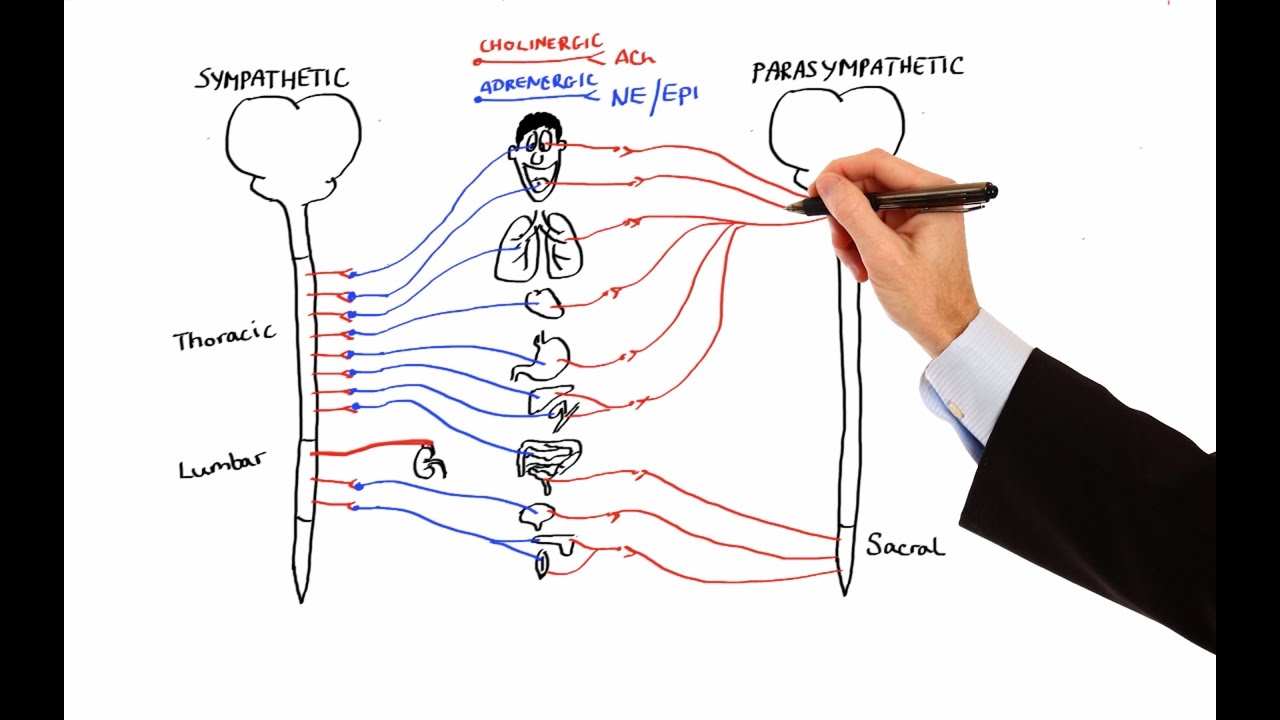
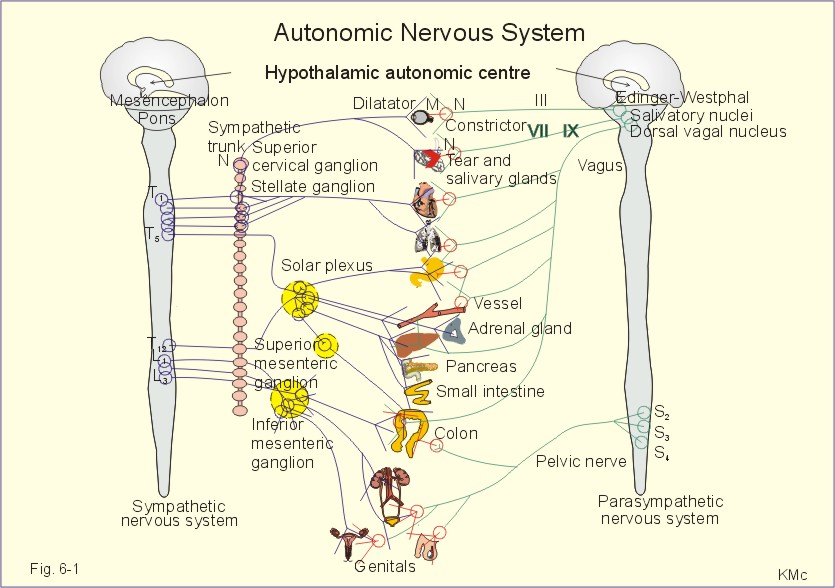
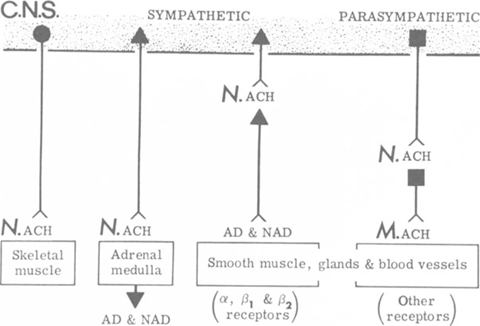
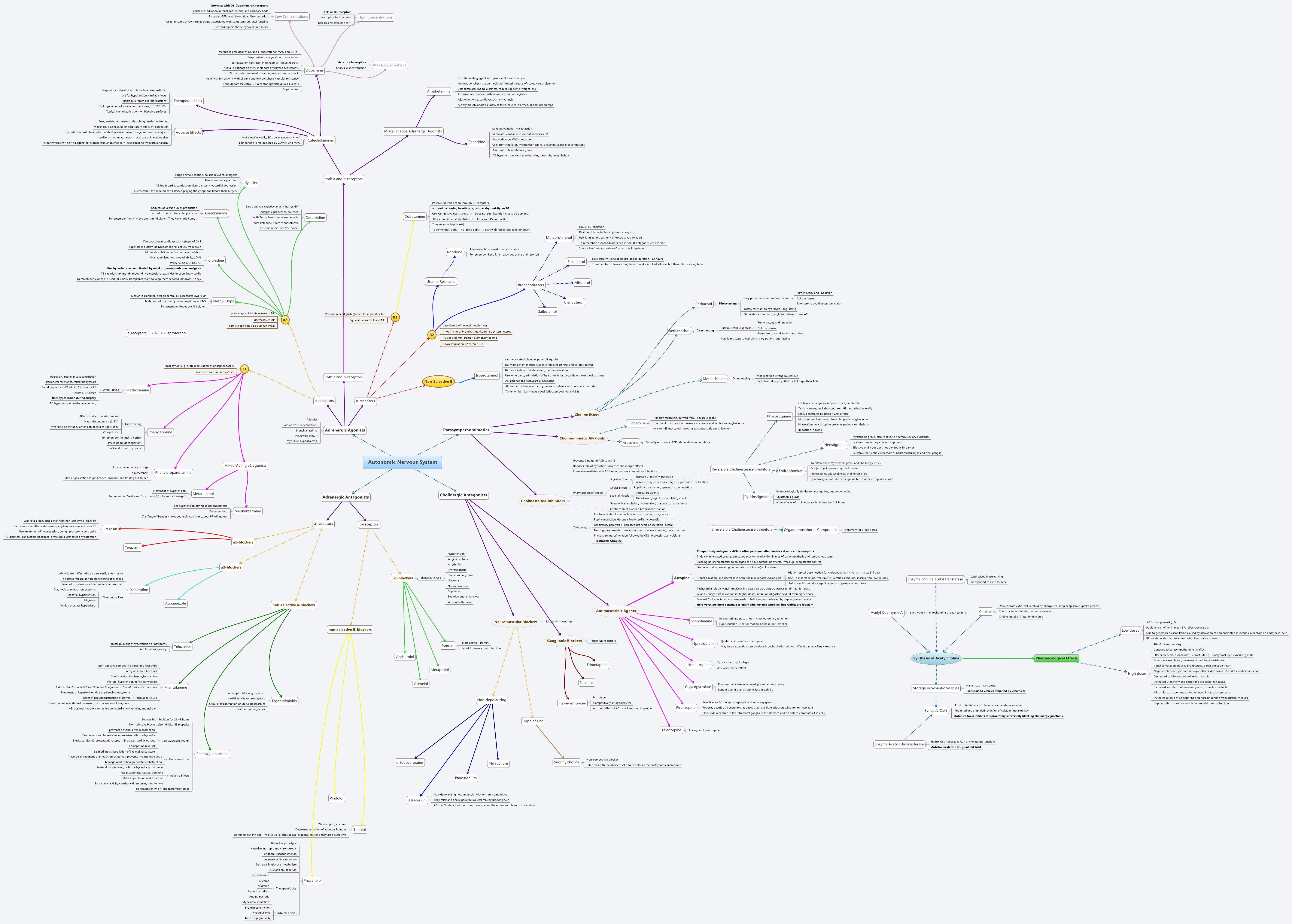
Autonomic nervous system pharmacology. Physiology and Pharmacology Loreta Grecu Key Points The autonomic nervous system ANS includes that part of the central and peripheral nervous system concerned with involuntary regulation of cardiac muscle smooth muscle glandular and visceral functions. The autonomic nervous system plays an important role in the control of the internal organs including the heart lungs gastrointestinal tract and vasculature. Autonomic Nervous System Visceral Efferent Nervous SYSTEM Involuntary Efferent motor.
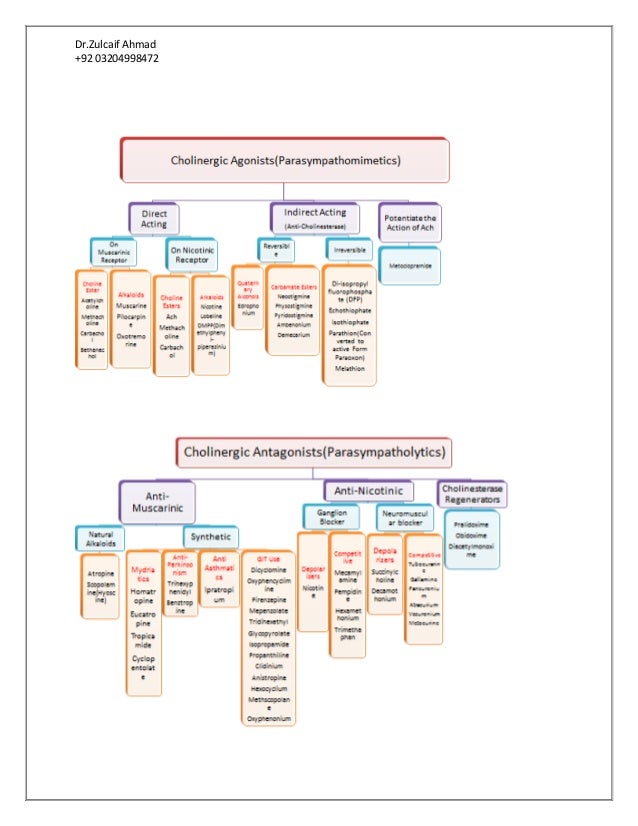
Autonomic Nervous System consists of. This overlies a strong circadian rhythm of autonomic. CHOLINERGIC AGONISTS General effects of cholinergic stimulation intoxication.
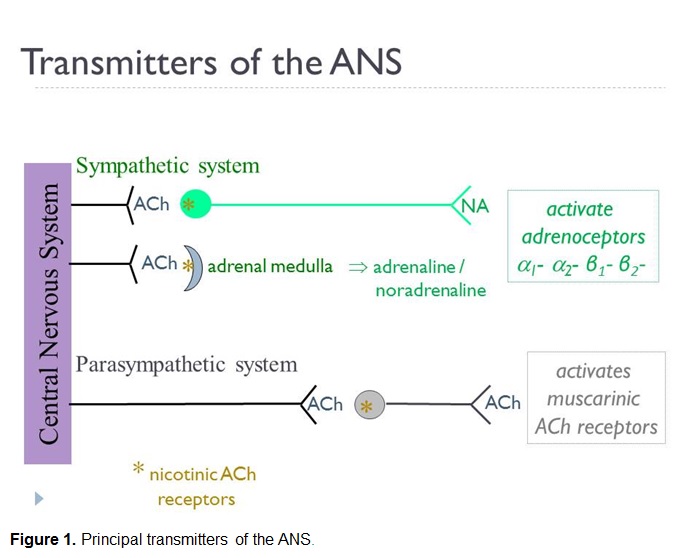
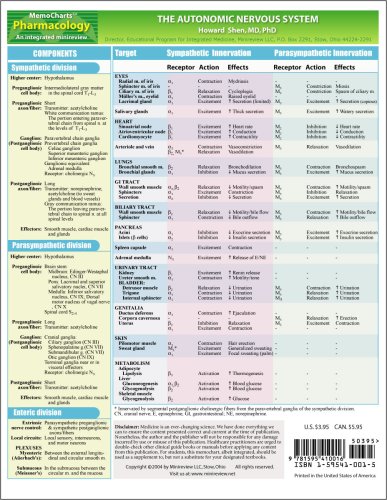
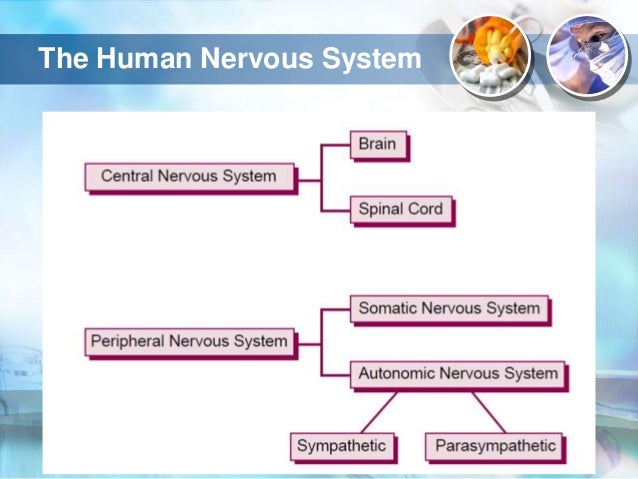
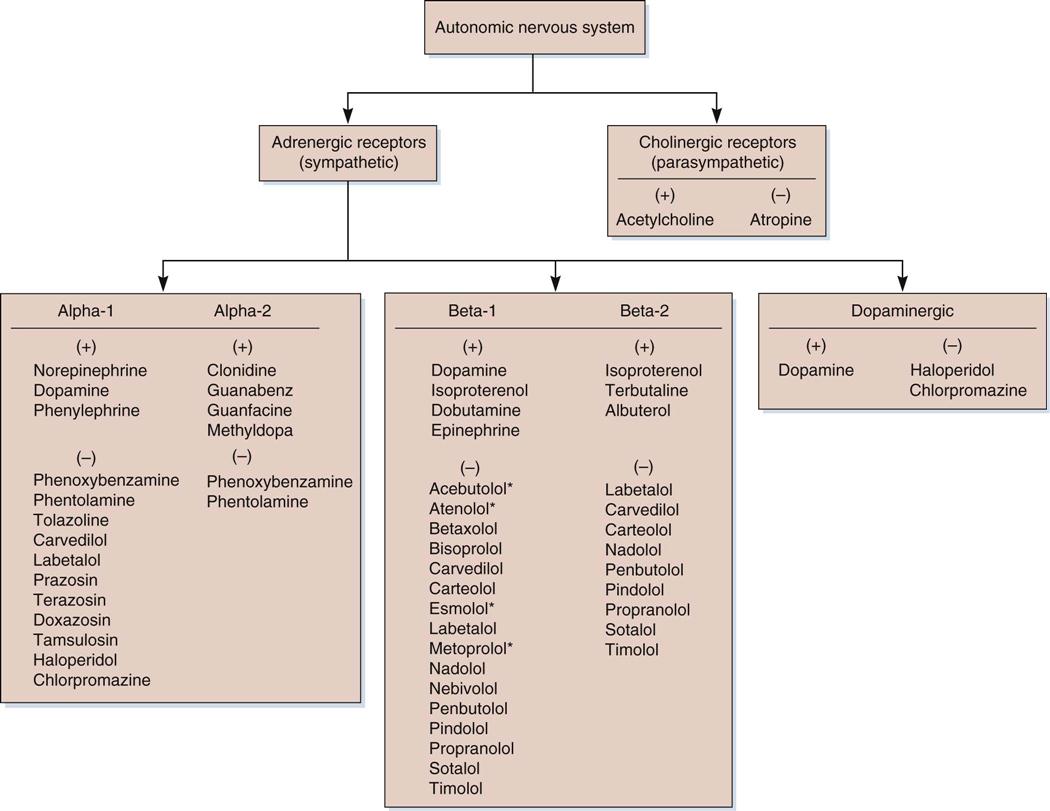
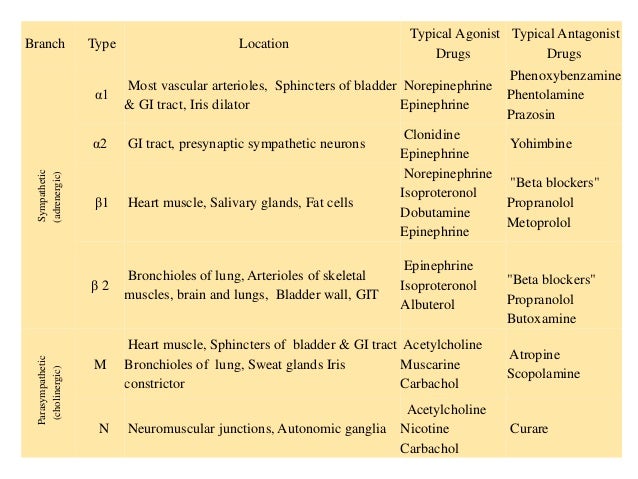
The SNS contains alpha and beta receptors and the PNS contains nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the sympathetic division SNS and the parasympathetic division PNS. Autonomic Nervous System.
You could not single-handedly going next book growth. The autonomic nervous system ANS works using a balance of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems that regulate the bodys involuntary functions including heart rate respiratory rate digestion and sweating. Drugs which target the autonomic nervous system are therefore useful in.
Its reaction to drugs is of interest from every angle of the practice of medicine. They are antagonistic in function on organs in a state of dynamic equilibrium. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
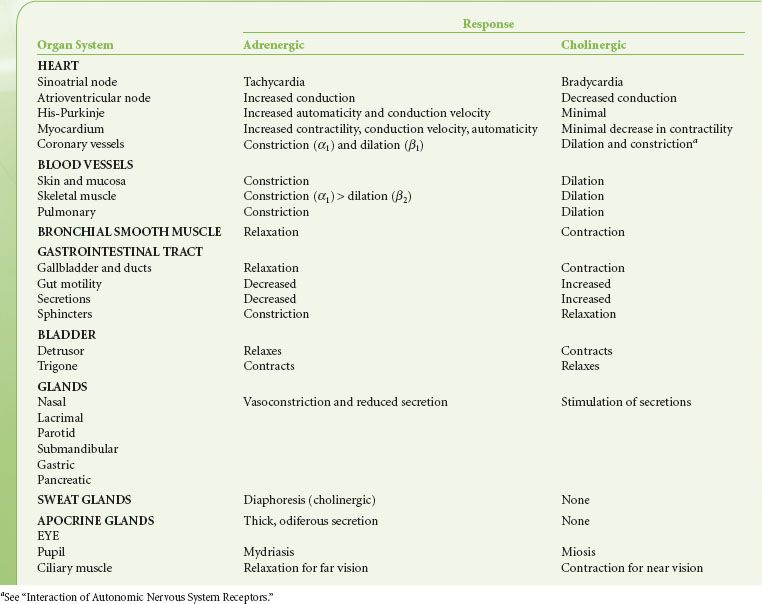
Miosis accommodation spasm blurred vision 3. Chapter 13 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PHARMACOLOGY 219 identified and subdivided into two primary types α and β according to their responses to epinephrine and norepineph-rine3 The β-receptors were further divided into β1- β2- and β3-receptors based on their actions at receptors and. Introduction The CNS receives diverse internal and external stimuli.
The autonomic nervous systemalso known as the visceral systeminvoluntarily regulates smooth muscles and glands including the heart respiratory system GI tract peristalsis digestion bladder and eyesThe autonomic nervous system has two sets of nerves. A large number of additional drug classes also interact with these systems to produce a stunning number of possible side effects.
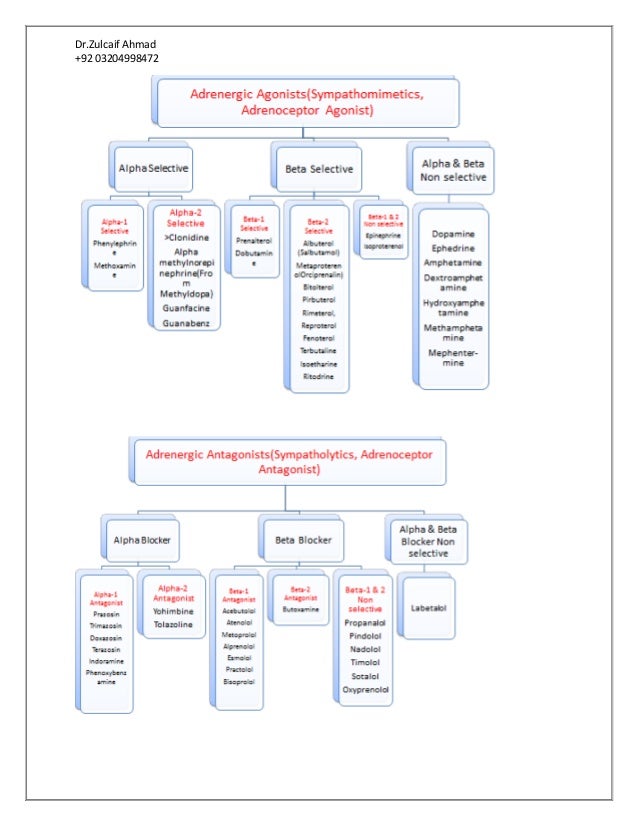
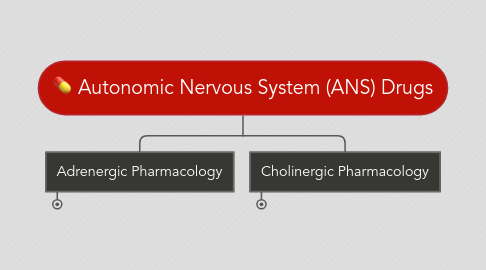
Autonomic drugs are used clinically to either imitate or inhibit the normal functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System. This article reviews the basic function of the autonomic nervous system and. Salivation sweating lacrimation 2. Chapter 13 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PHARMACOLOGY 219 identified and subdivided into two primary types α and β according to their responses to epinephrine and norepineph-rine3 The β-receptors were further divided into β1- β2- and β3-receptors based on their actions at receptors and. Autonomic pharmacology is the study of how drugs interact with the autonomic nervous system. Autonomic Nervous System. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Autonomic nervous system - pharmacology 1. Its reaction to drugs is of interest from every angle of the practice of medicine.
Pharmacology 501 January 10 12 2005 David Robertson MD. Drugs which target the autonomic nervous system are therefore useful in. Salivation sweating lacrimation 2. This article reviews the basic function of the autonomic nervous system and. Physiology and Pharmacology Loreta Grecu Key Points The autonomic nervous system ANS includes that part of the central and peripheral nervous system concerned with involuntary regulation of cardiac muscle smooth muscle glandular and visceral functions. Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous SystemDrugs That Act on Adrenergic Effector OrgansSympathomimetic DrugsFrom the foregoing discussion it is obvious that intravenous injection of norepinephrine causes essentially the same effects throughout the body as sympathetic stimulation. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems SNS PNS affect cardiac pump.































Post a Comment for "Autonomic Nervous System Pharmacology"